Hi 👋there,
Now we are on the Day 18 task
Docker-Compose Project for DevOps Engineers
Checkout the below link for Day 18 task:
https://github.com/LondheShubham153/90DaysOfDevOps/blob/master/2023/day18/tasks.md
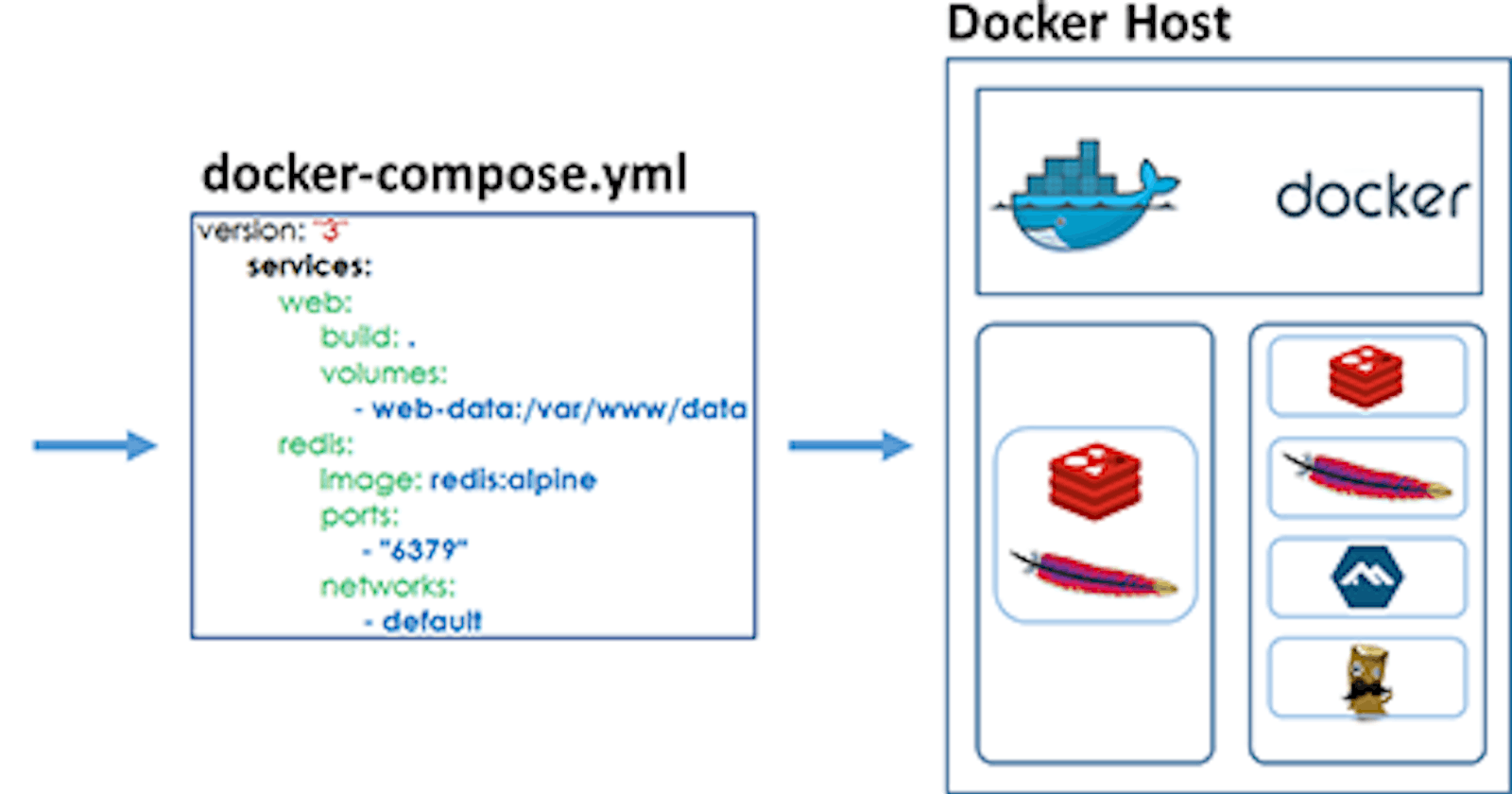
Docker Compose
Docker Compose is a tool that was developed to help define and share multi-container applications.
With Compose, we can create a YAML file to define the services and with a single command, can spin everything up or tear it all down.
To learn more about docker-compose visit here
What is YAML?
YAML is a data serialization language that is often used for writing configuration files. Depending on whom you ask, YAML stands for yet another markup language or YAML ain’t markup language (a recursive acronym), which emphasizes that YAML is for data, not documents.
YAML is a popular programming language because it is human-readable and easy to understand.
YAML files use a .yml or .yaml extension.
Read more about it here
Task-1
Learn how to use the docker-compose.yml file, to set up the environment, configure the services and links between different containers, and also to use environment variables in the docker-compose.yml file.
What is Docker-Compose?
Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. It allows you to define your application as a set of services, each with its own container, and specify how these containers should interact with each other.
With Docker Compose, you can define your application’s infrastructure, including databases, message queues, and web servers, in a simple YAML file.
Docker Compose provides a simple way to orchestrate and manage the containers that make up your application, allowing you to start and stop them together, scale them up and down as needed, and manage their network connections.
This makes it easier to develop, test, and deploy complex applications that consist of multiple services.
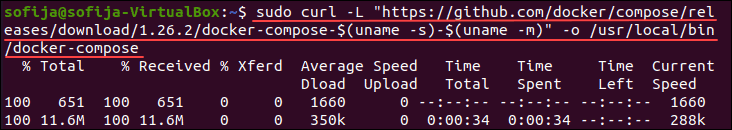
Step 1: Installing Docker-Compose in the server
Step 2: Create a docker-compose.yml file
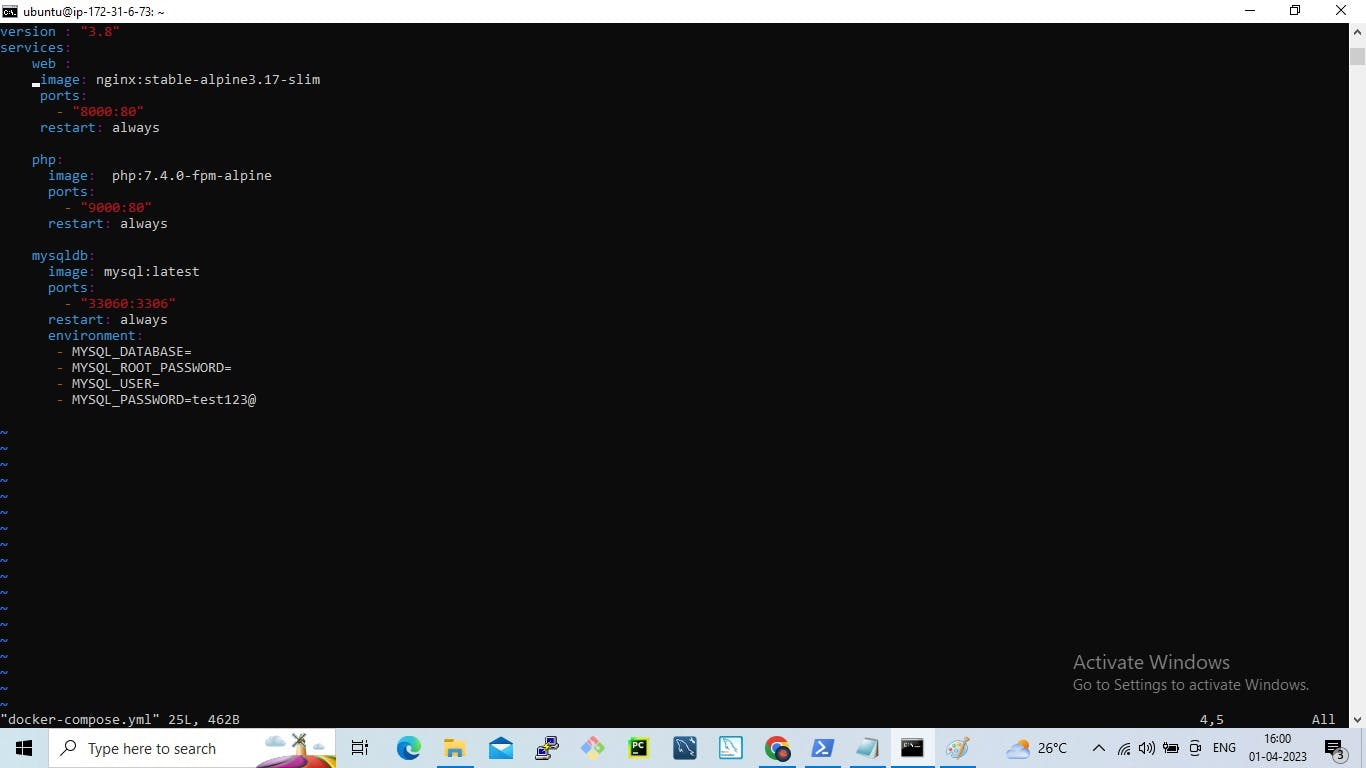
So now we will see all the things written in the docker-compose file.
version: 3.8 denotes that we are using version 3.8 of Docker Compose.
The service informs us about the various containers the compose file is going to create in this case three will be created as we have three services: web, PHP and mysqldb.
The image keyword is used to specify the image from the docker hub for MYSQL containers, Ngnix and Php
For all three services, we are using different ports and using the port keyword to mention the ports that need to expose for those services.
And then, we also specify the environment variables for MySQL which are required to run MySQL.
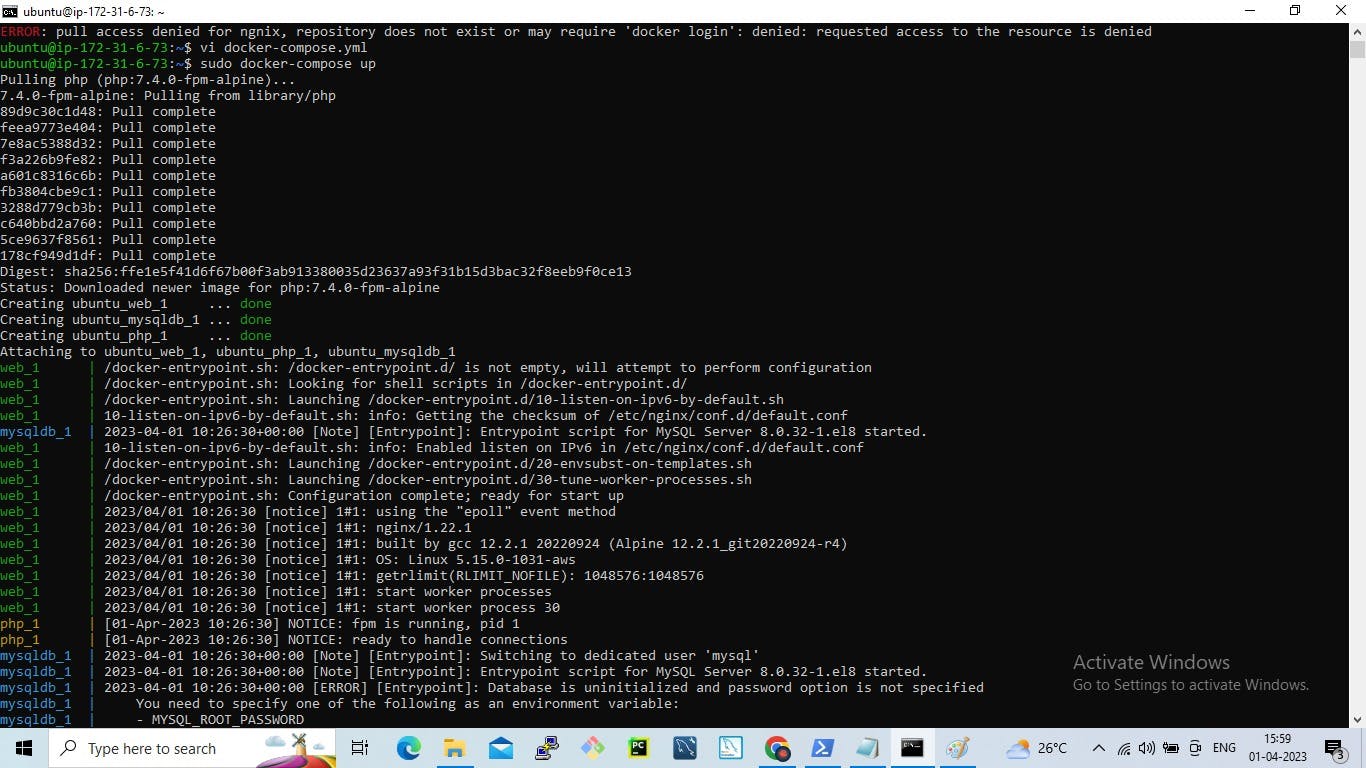
Step 3: Running the docker-compose.yml file
The docker-compose-up command is used to start up a set of containers defined in a Docker Compose file.
By default, docker-compose up starts containers in the foreground and logs their output to the console. You can use the -d flag to start the containers in detached mode, which runs them in the background.
The docker-compose ps command is used to display the status of containers defined in a Docker Compose file.
Step 4: Verify that the application is working on the web browser
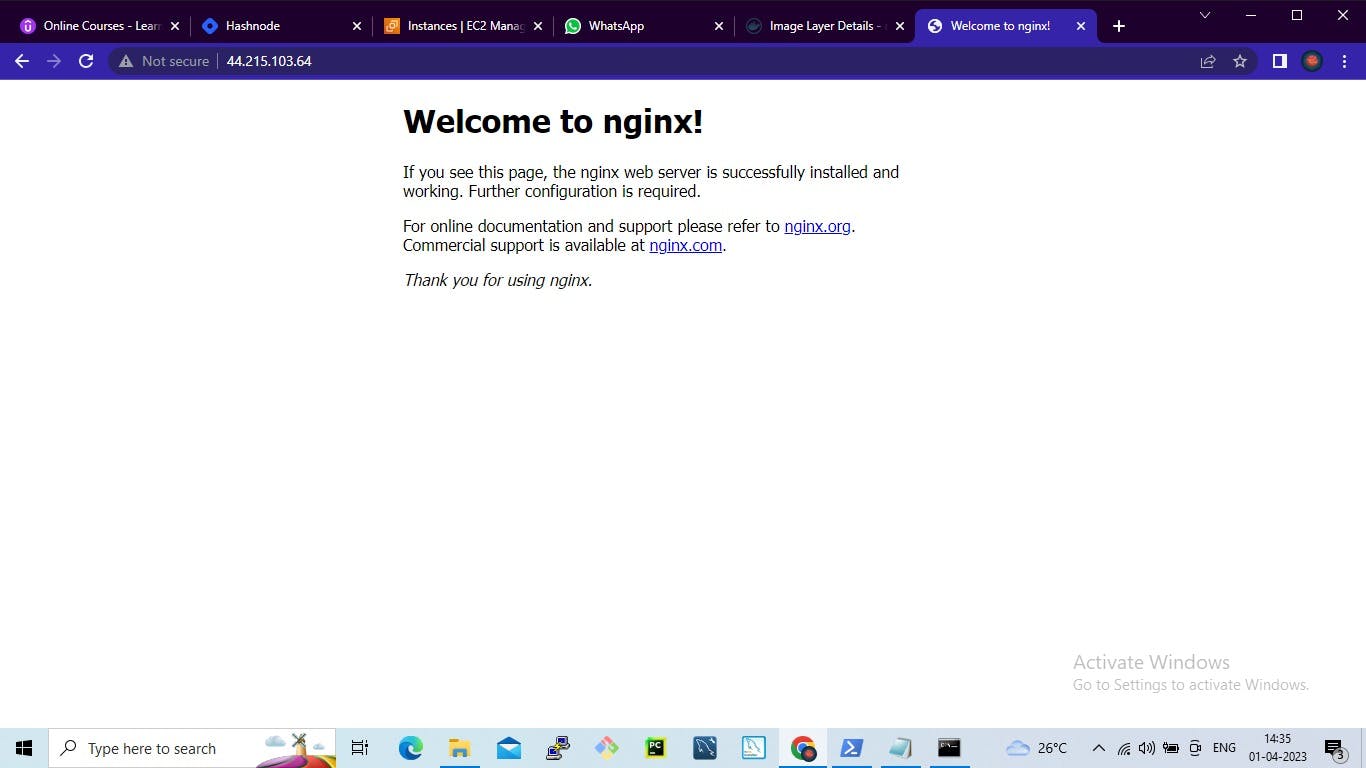
Task-2
- Pull a pre-existing Docker image from a public repository (e.g. Docker Hub) and run it on your local machine. Make sure you reboot the instance after permitting the user.

Run the container as a non-root user (Hint- Use
usermodcommand to give the user permission to docker).
Then reboot the instance after permitting the user.

Inspect the container’s running processes and exposed ports using the docker inspect command.
docker inspect <container_name or ID>
- Use the docker logs command to view the container’s log output.
docker logs <container_name or ID>
- Use the docker stop and docker start commands to stop and start the container.
docker stop <container-name or ID>
- Use the docker rm command to remove the container when you’re done.
docker start <container-name or ID>
Please, feel free to drop any questions in the comments below. I would be happy to answer them.
If you find this post helpful😊🙂, please follow and click the heart❤❤ button below to show your support.
_ Thank you for reading
_sandhya kumari